Labour Market Review
- Home
- Statistics
- Labour Market
- Labour Market Information
- Labour Market Review
Labour Market Review, Third Quarter 2021
Labour Market Review, Second Quarter 2021 21 May 2021
Labour Market Review, First Quarter 2021 18 February 2021
Labour Market Review, Fourth Quarter 2020 19 November 2020
Labour Market Review, Third Quarter 2020 19 August 2020
Labour Market Review, Second Quarter 2020 21 May 2020
Labour Market Review, First Quarter 2020 Show all release archives
Overview
Introduction
The Labour Market Review (LMR) is a quarterly release by Malaysian Bureau of Labour Statistics (MBLS), Department of Statistics, Malaysia (DOSM) that brings official statistics to life through reviews and features which highlighted the most recent trends in labour market. The quarterly statistics is consolidated in a narrative to provide readers with a comprehensive view on Malaysia’s labour market.
The report is divided into three segments to provide readers the different aspects of labour market information encompassing Labour Supply, Labour Demand and Labour Productivity. The special feature of the report is for every quarter, there is one or more article(s) highlighting the most recent labour market issues through statistics; or delving on the methodologies to strengthen labour market statistics.
The report will elaborate on the year-on-year changes as well as the short-term changes from the previous quarter to examine the immediate effect of recent events. Users are advised to interpret the quarterly changes with cautions since they are non-seasonally adjusted. The LMR can be used by policy makers, academicians, economists, researchers and other users for studies related to the labour market. It is hoped that this report can facilitate the growing demand for labour market statistics.
Key Reviews
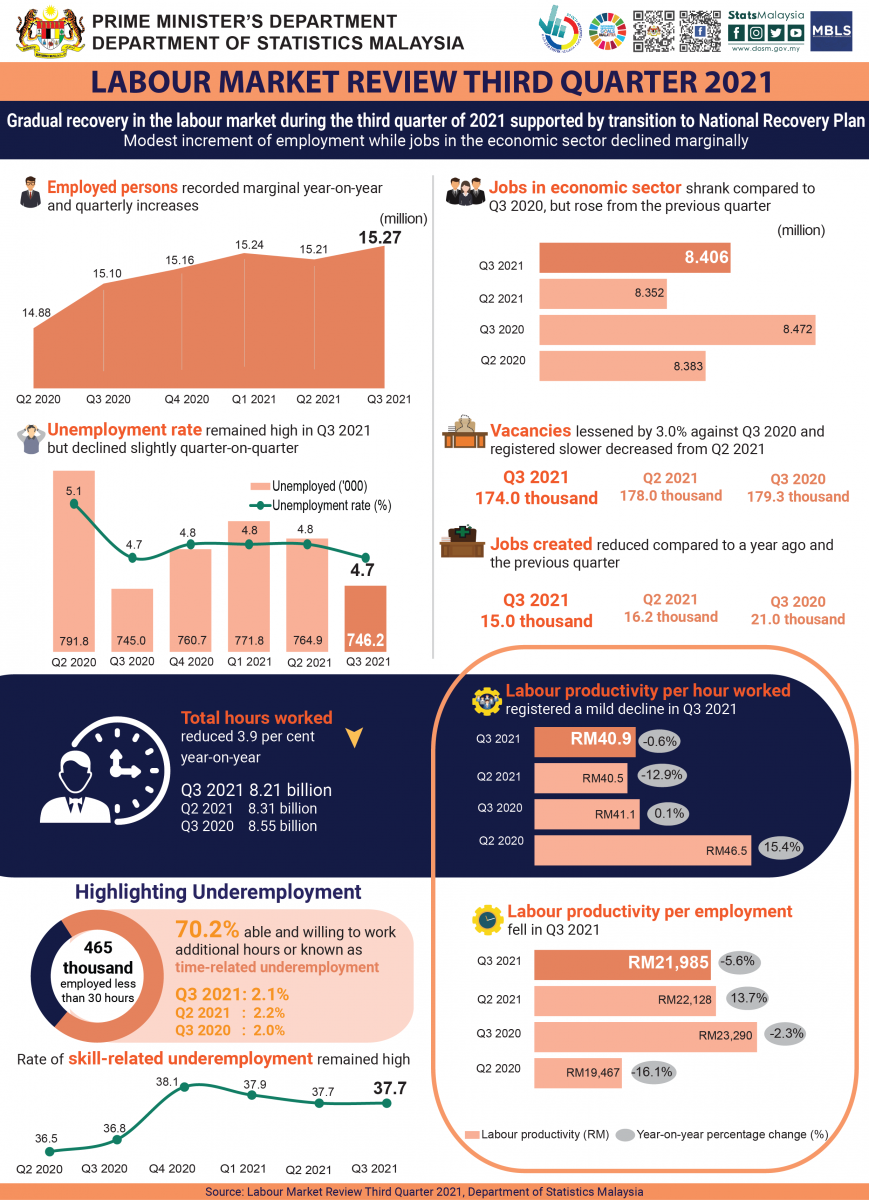
- In overall, employment improved at a moderate pace as against the previous year while unemployment rate remained unchanged amid continuous decline in labour demand. Hence, Malaysia’s labour market situation has yet to return to the pre-pandemic level in Q3 2021 albeit posting better quarter-on-quarter performance.
- In Q3 2021, the number of employed persons recorded a marginal increment of 1.2 per cent year-on-year compared to an annual rise of 2.2 per cent to record 15.27 million persons with employment-to-population ratio dropped 0.1 percentage point to 65.1 per cent. The unemployment rate remained elevated at 4.7 per cent whereby the number of unemployed persons rose marginally by 0.2 per cent to 746.2 thousand persons.
- As most states remained in either the first or second phase of the NRP, only between 60 to 80 per cent of private sector’s employees were allowed to work at-site on rotation basis. Thus, the number of employed persons working less than 30 hours per week increased 13.7 per cent compared to the same quarter in the previous year to record 464.6 thousand persons. Accordingly, the rate of time-related underemployment also rose to 2.1 per cent. Skill-related underemployment remained high at 37.7 per cent.
- In term of demand for labour in the economic sector, jobs continued to shrink 0.8 per cent as against a year ago to 8.406 million jobs during Q3 2021. Filled jobs which comprised of 97.9 per cent reduced by 0.7 per cent to record 8.232 million. Meanwhile jobs opening as reflected by the number of vacancies lessened 3.0 per cent to 174.0 thousand job vacancies during same period.
- As Malaysia’s economy slipped back into contraction of 4.5 per cent in Q3 2021 while employment registered a smaller increase, labour productivity per employment declined by 5.6 per cent while labour productivity per hour worked continued to drop albeit at an improved pace of negative 0.6 per cent. During the same period, total hours worked dropped 3.9 per cent to 8.21 billion hours following limited business operations. Labour productivity per hour worked continued to drop albeit at an improved pace of negative 0.6 per cent after two successive quarters of double-digit declines (Q2 2021: 12.9%).
- With the shrinking labour demand and increasing number of potential new entrants into the labour market, continuous reform is required in scaling up jobs opportunities. Hence, long term ideal interventions may enable better absorption of labour supply into the labour market, and ultimately guarantee rise in efficiency as well as better economic growth prospect. In this regard, seamless integration of macro statistical indicators and detailed labour market databases across agencies will provide a better chance at frequent and consistent monitoring of the labour market flow and stocks. Further to this, strategic collaborations between public and private sectors will also provide the nudge towards facilitating consistent talent and capacity building; as well as increasing investment in research and technology as part of the strategies to restructure the economy and facilitate skilled jobs creation.
- More than a month into Q4 2021, the public health situation appeared to be improving with the daily new cases reducing to four-digit. Accelerating vaccination efforts has partly attribute to the phase transition, hence allowing more economic activities to resume and selected restrictions to be lifted. With these recent positive developments, the economy is anticipated to regain and consequently influence more demand for labour as well as contribute towards better labour market situation in Q4 2021.

Download full LMR Q3 2021 publication here
The full publication of LMR Q3 2021 is also accessible and downloadable free of charge through the eStatistik application in DOSM web page, www.dosm.gov.my.
Released By:
DATO' SRI DR. MOHD UZIR MAHIDIN
CHIEF STATISTICIAN MALAYSIA
DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS, MALAYSIA
![]() DrUzir_Mahidin
DrUzir_Mahidin ![]()
![]() Dr_Uzir
Dr_Uzir
19 November 2021
Contact person:
Mohd Yusrizal Ab Razak
Public Relation Officer
Strategic Communication and International Division
Department of Statistics, Malaysia
Tel : +603-8885 7942
Fax : +603-8888 9248
Email : yusrizal.razak[at]dosm.gov.my
Subscribe
Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated
For interviews, press statement and clarification to the media, contact:
Baharudin Mohamad
Public Relation Officer
Email: baharudin[at]dosm.gov.my
Phone: 03 8090 4681
Not found what you looking for? Request data from us, through
Go to eStatistik
Email: data[at]dosm.gov.my
Phone: 03 8885 7128 (data request)










